Most of us glance at the clock, see the time, and move on with our day without ever questioning how that number is decided. Time zones are one of those invisible systems we all follow but rarely understand.
In this article, we’ll unravel the mysteries of time zones, what they are, why they exist, and how the world agreed to slice up the planet into different hours. From the United States and China to every continent across the globe, we’ll break it down step by step with maps, tables, and examples so you finally see how the world keeps its clocks in sync.
How to read time zone labels
When you see something like EST / EDT, UTC-05:00 / UTC-04:00, each part has a specific meaning:
| Part | Meaning |
|---|---|
| EST | Eastern Standard Time – the normal time setting used most of the year |
| EDT | Eastern Daylight Time – the adjusted setting in summer when clocks move forward one hour |
| UTC-05:00 | The zone is 5 hours behind Coordinated Universal Time, the world’s reference clock |
| UTC-04:00 | During daylight saving time the zone shifts to 4 hours behind UTC |
So basically, this just shows how a region’s clock compares to the world’s reference clock – either a set number of hours ahead or behind, sometimes shifting by one hour in summer.
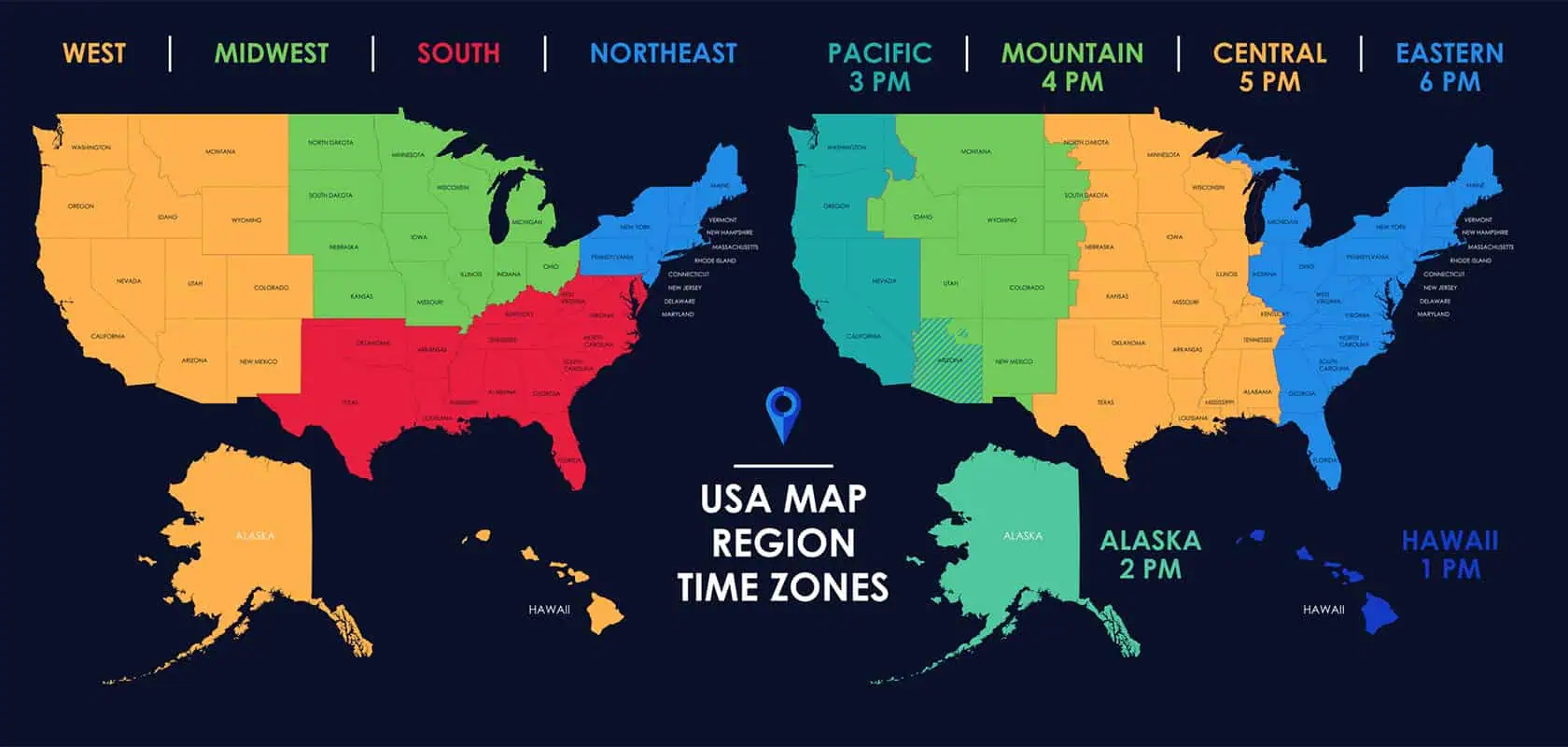
U.S. time zones
The United States is divided into six primary time zones to keep local time roughly aligned with the position of the sun. Each zone shifts the clock by one hour as you move west, creating a staggered system that helps daily routines stay consistent with daylight hours across the country.
The six U.S. time zones are Eastern, Central, Mountain, Pacific, Alaska, and Hawaii–Aleutian. These zones apply across the lower 48 states as well as Alaska and Hawaii, and most of them observe Daylight Saving Time for part of the year.
Eastern Time Zone (ET)
UTC offset: UTC−5 (UTC−4 during Daylight Saving Time)
Eastern Time is the earliest zone in the continental United States. It includes the entire East Coast and extends west into parts of states like Indiana, Kentucky, and Michigan. Major cities in this zone include New York City, Washington, D.C., Atlanta, Miami, Boston, and Philadelphia.
This time zone sets the national pace for business, finance, and media. The U.S. stock market runs on Eastern Time, and most national news broadcasts are timed to this schedule. It is often the reference point used when displaying times across multiple zones.
Central Time Zone (CT)
UTC offset: UTC−6 (UTC−5 during Daylight Saving Time)
Central Time is one hour behind Eastern and covers a wide range of states in the Midwest and South. These include Illinois, Texas, Minnesota, Missouri, Louisiana, and large parts of Oklahoma, Arkansas, and the Dakotas. Major cities include Chicago, Dallas, Houston, and New Orleans.
Central Time balances both urban and rural regions. It plays an important role in agriculture, transportation, and national sports scheduling. Many broadcasts in the U.S. use Central Time as their second primary listing after Eastern.
Mountain Time Zone (MT)
UTC offset: UTC−7 (UTC−6 during Daylight Saving Time)
Mountain Time is one hour behind Central and covers much of the interior West. States in this zone include Colorado, New Mexico, Utah, Wyoming, and parts of Arizona, Idaho, and Montana. Cities such as Denver, Salt Lake City, and Albuquerque use Mountain Time.
This zone has fewer people than Eastern and Central but spans large, scenic areas. Arizona is a notable exception within the zone, as most of the state does not observe Daylight Saving Time. That means during part of the year, Arizona lines up with Pacific Time instead.
Pacific Time Zone (PT)
UTC offset: UTC−8 (UTC−7 during Daylight Saving Time)
Pacific Time includes the West Coast states of California, Oregon, and Washington, as well as western Nevada. Cities like Los Angeles, San Francisco, Seattle, San Diego, and Las Vegas all fall within this zone.
This zone is especially important to the entertainment and tech industries. Many TV shows, streaming releases, and app launches are scheduled by Pacific Time. It is also the last major U.S. time zone before crossing into Alaska or international time zones.
Alaska Time Zone (AKT)
UTC offset: UTC−9 (UTC−8 during Daylight Saving Time)
The Alaska Time Zone covers nearly the entire state of Alaska, excluding some far-western islands. Anchorage, Juneau, and Fairbanks all observe Alaska Time. This zone is one hour behind Pacific Time.
Due to Alaska’s northern location, daylight hours can vary drastically with the seasons. Daylight Saving Time is observed here, although seasonal shifts are less noticeable during periods of extended light or darkness.
Hawaii–Aleutian Time Zone (HAT)
UTC offset: UTC−10 (no Daylight Saving Time in Hawaii)
This is the westernmost U.S. time zone and includes all of Hawaii along with the Aleutian Islands in Alaska. The largest city in this zone is Honolulu. Hawaii does not observe Daylight Saving Time.
Because Hawaii remains on standard time all year, the time difference from the mainland changes slightly depending on the season. During part of the year, Hawaii is five hours behind Eastern Time. In the summer months, that difference increases to six hours.
U.S. territories and their time zones
Several U.S. territories fall outside the six main time zones. Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands use Atlantic Standard Time (UTC−4) and do not observe Daylight Saving Time. This puts them one hour ahead of Eastern Time in the winter and the same time as Eastern during the summer.
Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands operate on Chamorro Standard Time (UTC+10), while American Samoa uses Samoa Standard Time (UTC−11). These territories are located far from the continental U.S. and follow their own timekeeping systems based on their position in the Pacific.
Canada time zones
Canada is a large country that spans six primary time zones from coast to coast. While several of these zones are shared with the United States, Canada also includes a couple of unique time zones not used anywhere else in North America. These include Atlantic Time and Newfoundland Time.
From the Pacific coast of British Columbia to the eastern edge of Newfoundland, time zones help organize travel, business, and communication across Canada’s vast geography. Most provinces and territories observe Daylight Saving Time, though there are exceptions in certain regions.
Pacific Time Zone (PT)
UTC offset: UTC−8 (UTC−7 during Daylight Saving Time)
The Pacific Time Zone in Canada covers the entire province of British Columbia and the Yukon territory. Cities like Vancouver, Victoria, and Whitehorse follow PT. This zone is shared with the U.S. West Coast, including cities like Seattle and Los Angeles.
British Columbia observes Daylight Saving Time, although some smaller communities have petitioned to stay on standard time year-round. Pacific Time plays a central role in coordinating trade and travel with the western United States.
Mountain Time Zone (MT)
UTC offset: UTC−7 (UTC−6 during Daylight Saving Time)
Mountain Time covers the provinces of Alberta and parts of the Northwest Territories, Saskatchewan, and British Columbia. Calgary and Edmonton are the largest cities in this zone. This time zone is shared with parts of the U.S. interior West, including Colorado and Utah.
Most areas observe Daylight Saving Time, except for certain portions of northeastern British Columbia and some border towns that align with their neighboring provinces for consistency.
Central Time Zone (CT)
UTC offset: UTC−6 (UTC−5 during Daylight Saving Time)
Central Time is used in the province of Manitoba and portions of northwestern Ontario and eastern Saskatchewan. Winnipeg is the major city in this zone. Like in the U.S., this zone is centered on the central part of the continent.
Saskatchewan is unique because most of the province does not observe Daylight Saving Time and stays on Central Standard Time all year. This can cause confusion during seasonal changes when nearby regions adjust their clocks.
Eastern Time Zone (ET)
UTC offset: UTC−5 (UTC−4 during Daylight Saving Time)
Eastern Time covers southern Ontario, southern Quebec, and parts of Nunavut. Cities like Toronto, Ottawa, Montreal, and Quebec City use Eastern Time. This is the same time zone used by the U.S. East Coast.
Eastern Time is the most populated time zone in Canada and plays a central role in business, politics, and national media. Most areas observe Daylight Saving Time and follow the same schedule as the U.S.
Atlantic Time Zone (AT)
UTC offset: UTC−4 (UTC−3 during Daylight Saving Time)
Atlantic Time is used in the eastern provinces of New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island. Cities like Halifax, Fredericton, and Charlottetown operate on this time. This zone is not used anywhere in the continental U.S., but it does match the time used in Puerto Rico during standard time.
This time zone helps account for the earlier sunrises and sunsets in the Maritime provinces. Atlantic Time is especially important for coordinating coastal shipping, fishing industries, and transatlantic travel connections.
Newfoundland Time Zone (NT)
UTC offset: UTC−3:30 (UTC−2:30 during Daylight Saving Time)
Newfoundland Time is unique to the island of Newfoundland and parts of southeastern Labrador. The largest city in this zone is St. John’s. It is the only time zone in North America that uses a half-hour offset.
This unusual offset allows the region to better align its daylight hours with the local sunrise and sunset. Most of the province observes Daylight Saving Time, keeping the same half-hour lead during seasonal changes.
Latin America time zones
Between Mexico, Central America, and South America, you’ll find at least seven distinct time zones ranging from UTC−8 to UTC−2:30. Some countries observe daylight saving time, while others stay on a fixed schedule year-round. Despite overlapping offsets, each region has its own approach to timekeeping based on geography, politics, and local needs. In this section, we break down the time zones used throughout Latin America and how they compare to global standards.
Pacific Time Zone (PT)
UTC offset: UTC−8 (no daylight saving)
In Mexico, the Pacific Time Zone is used in the northwestern state of Baja California. This zone matches the U.S. Pacific Time used in California and other western states. Major cities like Tijuana operate on this time, and it plays a role in cross-border travel and business with the U.S.
Mountain Time Zone (MT)
UTC offset: UTC−7 (no daylight saving in Sonora)
Several northern states in Mexico, including Chihuahua and Sonora, follow Mountain Time. However, Sonora does not observe daylight saving time, which keeps it aligned with Arizona all year. This makes scheduling consistent in a region that sees heavy U.S.-Mexico trade.
Central Time Zone (CT)
UTC offset: UTC−6 (UTC−5 during Daylight Saving Time)
The majority of Mexico uses Central Time, including Mexico City, Guadalajara, and Monterrey. This zone matches U.S. Central Time and is important for business hours, national news, and transportation schedules. Some areas observe daylight saving, though implementation may vary.
Eastern Time Zone (ET)
UTC offset: UTC−5 (no daylight saving)
The southeastern state of Quintana Roo, including cities like Cancún and Playa del Carmen, observes Eastern Time year-round. This time zone does not shift with daylight saving and aligns with places like Jamaica and parts of Colombia.
Central America
UTC offset: UTC−6 (no daylight saving)
Countries in Central America, including Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica, all use UTC−6 consistently throughout the year. This matches U.S. Central Standard Time but does not change for daylight saving.
Panama
UTC offset: UTC−5 (no daylight saving)
Panama follows UTC−5 year-round, the same as Eastern Standard Time, but it does not shift for daylight saving. This keeps it aligned with Colombia and parts of the Caribbean throughout the year.
Amazon Time
UTC offset: UTC−4
Used in Bolivia and western Brazil, Amazon Time covers large forested and interior regions. Cities like La Paz and Manaus follow this time. Daylight saving is not widely observed in this zone.
Brasília Time
UTC offset: UTC−3
This is the most widely used time zone in Brazil, covering cities like Brasília, São Paulo, and Rio de Janeiro. Argentina and Uruguay also use UTC−3, though they typically do not observe daylight saving time.
Chile Time
UTC offset: UTC−4 (UTC−3 during Daylight Saving Time)
Chile uses UTC−4 as its standard, with a summer shift to UTC−3. The capital city Santiago follows this schedule. This is one of the few countries in South America that observes daylight saving time.
Venezuelan Time
UTC offset: UTC−4:30
Venezuela uses a unique offset of UTC−4:30 year-round. This half-hour time difference sets it apart from neighboring countries and was established as a political and cultural distinction from other time zones in the region.
Colombia, Peru, Ecuador
UTC offset: UTC−5
These countries follow the same time zone year-round with no daylight saving time. Major cities like Bogotá, Lima, and Quito all operate on this schedule, which is the same as Eastern Standard Time in the U.S. during winter months.
Europe time zones
Across Europe, you’ll find four primary time zones ranging from UTC+0 to UTC+3. Most countries follow a shared daylight saving schedule, moving clocks forward one hour in late March and back again in late October. While many time zones overlap across borders, regional naming and usage still vary. Below we break down the major time zones in Europe and how they function across countries.
Western European Time (WET)
UTC offset: UTC+0 (UTC+1 during Daylight Saving Time)
Western European Time is used in countries like Portugal and Ireland. The United Kingdom also follows this time zone but often refers to it as GMT in winter and BST (British Summer Time) during daylight saving. Iceland also uses UTC+0 year-round, even though it does not observe daylight saving. Despite its western location, Iceland aligns its clocks with this European standard.
Central European Time (CET)
UTC offset: UTC+1 (UTC+2 during Daylight Saving Time)
This is the most widely used time zone in Europe. It includes countries such as France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Poland, Austria, Switzerland, and many others in central and western Europe. During summer months, clocks are shifted one hour forward to Central European Summer Time (CEST). This zone is a key standard for European business hours and travel networks.
Eastern European Time (EET)
UTC offset: UTC+2 (UTC+3 during Daylight Saving Time)
Eastern European Time is used in countries like Finland, Greece, Romania, Bulgaria, Ukraine, and the Baltic states (Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania). Like CET, this zone also follows daylight saving time, switching to Eastern European Summer Time (EEST) during warmer months. It’s commonly used in Eastern EU countries and aligns with Moscow time during summer.
Further East (Russia, Belarus, Turkey)
UTC offset: UTC+3 (no daylight saving)
Some parts of Eastern Europe and western Russia use UTC+3 year-round. Belarus and Turkey also operate on UTC+3 without observing daylight saving time. This time zone is sometimes referred to as Moscow Standard Time (MSK). While it overlaps with Eastern European Summer Time, countries in this group do not change their clocks during the year.
Africa time zones
Africa spans six main time zones, from UTC−1 to UTC+4. Most African countries do not observe daylight saving time, making local time relatively consistent year-round. Several large regions share the same zone, which simplifies scheduling within the continent but creates some unique overlaps across borders. Below is a breakdown of the key time zones used throughout Africa.
Cape Verde Time (CVT)
UTC offset: UTC−1 (no daylight saving)
The islands of Cape Verde are the only part of Africa using UTC−1. This makes them one hour behind most of mainland West Africa. The country does not observe daylight saving time and stays on this offset year-round.
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT)
UTC offset: UTC±0 (no daylight saving)
Several West African countries, including Ghana, Côte d’Ivoire, Togo, and The Gambia, use Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). These countries do not shift their clocks throughout the year, making timekeeping stable. This zone aligns with Western Europe during the winter but does not change in summer.
West Africa Time (WAT)
UTC offset: UTC+1 (no daylight saving)
This time zone covers Nigeria, Angola, Algeria, Cameroon, and several other countries across Central and Western Africa. Despite spanning large distances, these countries remain on UTC+1 year-round. WAT overlaps with Central European Time during the winter months.
Central Africa Time (CAT)
UTC offset: UTC+2 (no daylight saving)
Central Africa Time is used by countries such as South Africa, Zambia, Zimbabwe, Botswana, Malawi, and Mozambique. This zone also includes Egypt and Sudan. It matches Eastern European Time during winter but does not observe daylight saving time, so it differs during the summer.
East Africa Time (EAT)
UTC offset: UTC+3 (no daylight saving)
East Africa Time is used in Kenya, Ethiopia, Tanzania, Somalia, Uganda, and Madagascar. It remains consistent year-round with no daylight saving time. This zone also matches Moscow Time and Arabian Standard Time.
Mauritius Time (MUT) and Seychelles Time (SCT)
UTC offset: UTC+4 (no daylight saving)
These two Indian Ocean island nations use UTC+4 all year. While not as commonly referenced as continental time zones, they are important for regional coordination and are ahead of the rest of mainland Africa by one hour.
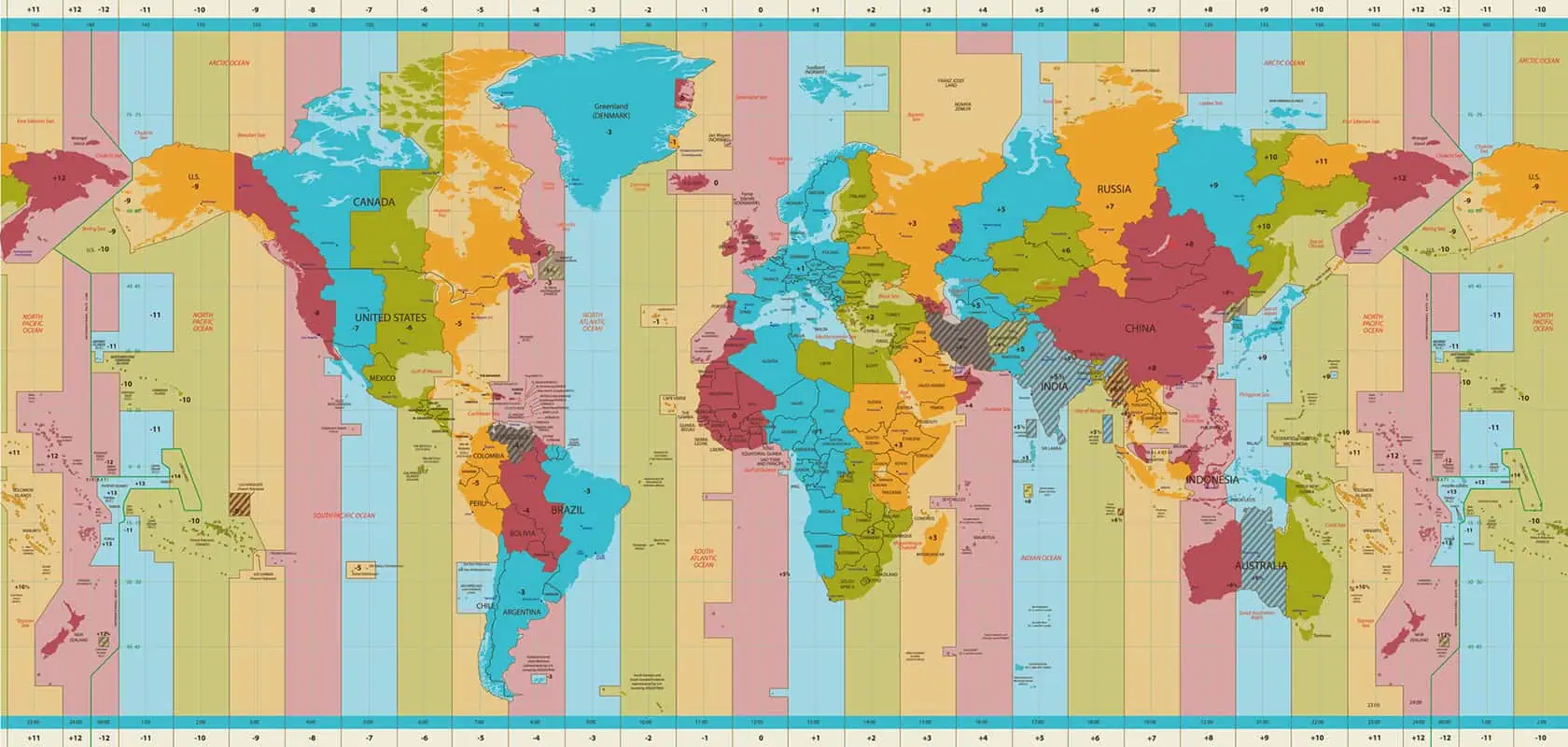
Asia time zones
Asia spans at least eleven different time zones, from UTC+2 to UTC+12, including several unique half-hour and quarter-hour offsets. It includes the largest country on Earth (Russia), the most populous (China and India), and some of the most unusual timekeeping policies in the world. Some countries span multiple time zones, while others—like China—use a single time zone across their entire territory. Below is a breakdown by region.
Middle East
Israel Standard Time (IST)
UTC offset: UTC+2 (UTC+3 during Daylight Saving Time)
Israel uses UTC+2 in winter and observes daylight saving time in summer, shifting to UTC+3. This is aligned with Eastern European Time and Eastern European Summer Time during those periods.
Arabian Standard Time (AST)
UTC offset: UTC+3 (no daylight saving)
Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Kuwait, Qatar, and Bahrain all follow Arabian Standard Time year-round without any daylight saving time.
Iran Standard Time (IRST)
UTC offset: UTC+3:30 (UTC+4:30 during Daylight Saving Time)
Iran uses a unique half-hour offset and also observes daylight saving time, switching to UTC+4:30 in summer. It’s one of the few countries that shifts both a non-whole-hour base and uses DST.
South Asia
Pakistan Standard Time (PKT)
UTC offset: UTC+5 (no daylight saving)
Pakistan follows UTC+5 year-round with no daylight saving adjustments.
India Standard Time (IST)
UTC offset: UTC+5:30 (no daylight saving)
India uses a half-hour offset and follows UTC+5:30 all year. This unique zone is shared by Sri Lanka as well. Despite its size, India uses only one time zone across the entire country.
Nepal Standard Time (NPT)
UTC offset: UTC+5:45 (no daylight saving)
Nepal has one of the world’s most unusual offsets at UTC+5:45. It stays consistent year-round and is 15 minutes ahead of India.
Central Asia
Kazakhstan Time Zones
UTC offset: UTC+5 and UTC+6 (no daylight saving)
Kazakhstan spans two time zones: western regions use UTC+5, and eastern regions use UTC+6. The country does not observe daylight saving time.
Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan
UTC offset: UTC+5 (no daylight saving)
These Central Asian countries follow UTC+5 and do not observe daylight saving time.
Kyrgyzstan Standard Time
UTC offset: UTC+6 (no daylight saving)
Kyrgyzstan remains on UTC+6 year-round with no seasonal changes.
East Asia
China Standard Time (CST)
UTC offset: UTC+8 (no daylight saving)
Despite spanning five geographical time zones, China uses a single national time—China Standard Time, set to UTC+8. This applies to all provinces, including far western regions like Xinjiang.
Japan Standard Time (JST)
UTC offset: UTC+9 (no daylight saving)
Japan uses UTC+9 year-round and does not observe daylight saving time. This time zone is also used in South Korea and some parts of eastern Russia.
Korea Standard Time (KST)
UTC offset: UTC+9 (no daylight saving)
South Korea follows UTC+9 without any daylight saving. It is aligned with Japan and part of far eastern Russia.
Southeast Asia
Indochina Time (ICT)
UTC offset: UTC+7 (no daylight saving)
Thailand, Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos all use UTC+7. There are no seasonal changes in this zone.
Malaysia Time (MYT) and Singapore Standard Time (SGT)
UTC offset: UTC+8 (no daylight saving)
Malaysia and Singapore both follow UTC+8 throughout the year. Brunei also uses this time zone.
Philippine Standard Time (PHT)
UTC offset: UTC+8 (no daylight saving)
The Philippines uses UTC+8 and does not observe daylight saving. It shares this time with much of East and Southeast Asia.
Indonesia Time Zones
UTC offset: UTC+7 to UTC+9 (no daylight saving)
Indonesia spans three time zones: Western Indonesia Time (UTC+7), Central Indonesia Time (UTC+8), and Eastern Indonesia Time (UTC+9). Each region uses its own fixed offset without seasonal changes.
Russia (Asian portion)
UTC offset: UTC+5 to UTC+12 (no daylight saving)
Russia spans eleven time zones total, with UTC+3 to UTC+12 covering the Asian portion. These zones include Yekaterinburg Time (UTC+5), Omsk Time (UTC+6), Krasnoyarsk Time (UTC+7), Irkutsk Time (UTC+8), Yakutsk Time (UTC+9), Vladivostok Time (UTC+10), Magadan Time (UTC+11), and Kamchatka Time (UTC+12). Russia no longer observes daylight saving time, so all regions stay on standard time throughout the year.
Oceania time zones
Oceania spans at least six main time zones from UTC+8 to UTC+14, including some of the most extreme and earliest time offsets on Earth. The region includes Australia, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, and dozens of island nations scattered across the Pacific. Several countries observe daylight saving time, while others stay fixed year-round. This region also contains the International Date Line, which causes some islands to operate nearly a full day ahead of others.
Western Standard Time (AWST)
UTC offset: UTC+8 (no daylight saving)
Western Australia, including Perth, operates on Australian Western Standard Time year-round. It does not observe daylight saving time and remains consistent with much of Southeast Asia.
Central Standard Time (ACST)
UTC offset: UTC+9:30 (UTC+10:30 during Daylight Saving Time)
South Australia and the Northern Territory use Australian Central Standard Time. South Australia observes daylight saving time, but the Northern Territory does not, which leads to temporary mismatches between the two.
Eastern Standard Time (AEST)
UTC offset: UTC+10 (UTC+11 during Daylight Saving Time)
This is the most common time zone in Australia, used by New South Wales, Victoria, Queensland, and Tasmania. All except Queensland observe daylight saving time. AEST aligns with Papua New Guinea and some Pacific islands outside the DST period.
Lord Howe Standard Time (LHST)
UTC offset: UTC+10:30 (UTC+11 during Daylight Saving Time)
Lord Howe Island, part of New South Wales, has a unique offset of UTC+10:30 and shifts to UTC+11 in summer. It’s one of the few half-hour DST changes in the world.
New Zealand Standard Time (NZST)
UTC offset: UTC+12 (UTC+13 during Daylight Saving Time)
New Zealand follows UTC+12 and shifts to UTC+13 in the summer months. This includes the main islands and surrounding territories like the Cook Islands and Tokelau. Clocks move forward in September and back in April.
Chatham Islands Time (CHAST)
UTC offset: UTC+12:45 (UTC+13:45 during Daylight Saving Time)
The Chatham Islands, part of New Zealand, have one of the most unusual time zones in the world. They are 45 minutes ahead of New Zealand’s mainland and also observe daylight saving time, shifting to UTC+13:45 in summer.
Pacific Island Time Zones
UTC offset: UTC+11 to UTC+14 (no daylight saving)
Island nations such as Fiji, Tonga, Vanuatu, the Solomon Islands, and Kiribati use a range of advanced time zones. Some of these locations, such as Tonga and parts of Kiribati, are among the first places on Earth to enter a new calendar day, operating as far ahead as UTC+14.
Unusual and remote time zones
Some time zones around the world fall outside standard hourly offsets, exist in polar regions, or are tied to political decisions rather than longitude. While these are less common, they highlight how timekeeping is often influenced by culture, geography, or even symbolism.
Nepal Standard Time (NPT)
UTC offset: UTC+5:45
Nepal operates on a unique offset that places it 15 minutes ahead of Indian Standard Time. This time zone is used throughout the country year-round without daylight saving time.
Venezuelan Standard Time (VET)
UTC offset: UTC−4:30
Venezuela previously used UTC−4 but now follows a −4:30 offset to reflect local solar time. This change was made for energy and political reasons and applies year-round.
Chatham Islands Time (CHAST)
UTC offset: UTC+12:45 (already covered above)
Repeated here due to its uniqueness — a 45-minute offset combined with daylight saving makes the Chatham Islands stand out globally.
Antarctica
UTC offset: Varies by research station
Antarctica has no official time zones of its own. Stations typically use the time zone of the country that operates them. For example, McMurdo Station uses New Zealand time, while some others follow Chilean or Argentine time. During summer months, daylight can last 24 hours, so clock time is more symbolic than functional.
UTC+14 (Line Islands, Kiribati)
UTC offset: UTC+14
Some of the Line Islands in Kiribati use UTC+14, the highest time zone offset in the world. This allows them to be among the first to experience each new day, even though they are not far from the International Date Line.
Common questions about time zones
How many time zones are there in the world?
There are 24 standard time zones, but when you include unusual offsets like UTC+5:45 or UTC+12:45, there are over 38 recognized time zones used around the world.
Which country has the most time zones?
France has the most time zones if you count its overseas territories — a total of 12. If you’re only counting mainland areas, then Russia has the most with 11 time zones across its vast landmass.
Why doesn’t China have multiple time zones?
China is large enough for five time zones, but the entire country officially uses one: China Standard Time (UTC+8). This was chosen to promote unity and simplify scheduling across regions.
Do all countries use time zones?
Yes, every country aligns with some form of time zone based on UTC, but not all use daylight saving time or follow standard hourly offsets. Some have half-hour or even 45-minute differences.
Why do some places ignore daylight saving time?
Many countries near the equator don’t use daylight saving time because their daylight hours don’t change much throughout the year. Others have stopped using it due to energy concerns or public dislike.
What if the world didn’t use time zones?
If the whole world used a single global time — like UTC — clocks would be the same everywhere, but daily life would feel totally off. In some places, sunrise might happen at 2 AM, while others would be eating dinner at what the clock says is 7 in the morning. Noon wouldn’t mean “midday” anymore — just a number on a clock disconnected from the sun.
Imagine this: It’s 9:00 AM everywhere in the world. In New York, the sun is rising and people are starting their workday. But in Tokyo, 9:00 AM is the middle of the night. Kids would be going to school at what the clock says is 10:00 PM. In Sydney, the sun might not set until 4:00 AM. Daily routines would stay the same, but the clock would always feel wrong.
Time zones exist to keep our clocks in sync with the sky. They make sure that 7 AM feels like morning and 8 PM feels like evening, no matter where you are. Without them, the world might be simpler on paper, but daily life would get a lot more confusing.
WildlifeInformer.com is your #1 source for free information about all types of wildlife and exotic pets. We also share helpful tips and guides on a variety of topics related to animals and nature. Subscribe on YouTube for videos.